IOT-Home Security And Automation
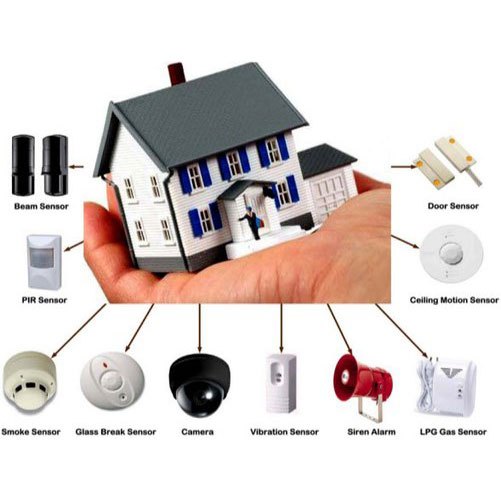

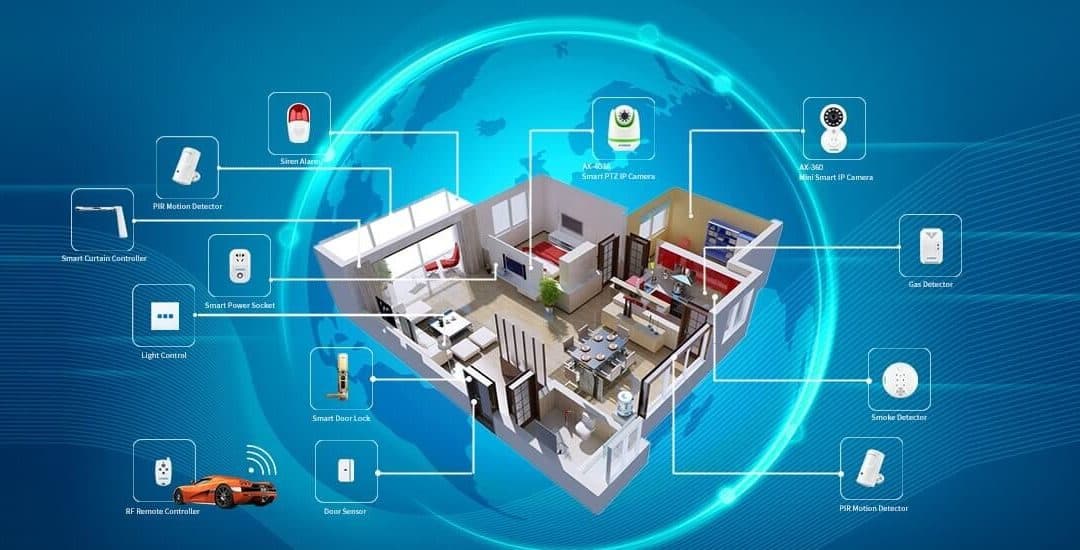
Home Automation And Security
IOT has transformed home security and automation by connecting devices using various wireless protocols. This allows remote monitoring and control of systems via apps.
Key Protocols:
– Z-Wave: Enables low-power wireless communication between devices like alarms, cameras, locks, lights, sensors up to 30 meters. Reliable for small/medium homes.
– Zigbee: Similar to Z-Wave but with 100m range and support for larger networks. Used in thermostats, sprinklers, energy monitors etc.
– WiFi: Devices connect to the home router for functions like streaming video from cameras and controlling smart speakers. Less secure than Z-Wave/Zigbee.
– Bluetooth: Short-range protocol for connecting accessories like key fobs, tags, remotes to the main hub/gateway.
– RF: Older systems use radio frequencies like 433MHz for functions like garage door openers. Now integrating with hubs.
– Powerline: Devices communicate through the home’s electrical wiring for long-range connectivity without WiFi dependence.
– MQTT: Popular lightweight IoT protocol to connect a central broker to various publishing devices/clients seamlessly through an open publishing/subscription model.
Key Devices:
Motion/entry sensors, smart locks, alarm panels, security cameras, glass breaks, smoke/flood sensors, lights/switches, thermostats etc work together secured by encryption on different protocols monitored through apps/voice assistants.
The future is seamless integration of all home systems on a unified platform for ultimate convenience, energy efficiency and around-the-clock security monitoring. Once huge data is collected we can perform data analytics and machine learning on top of them.
